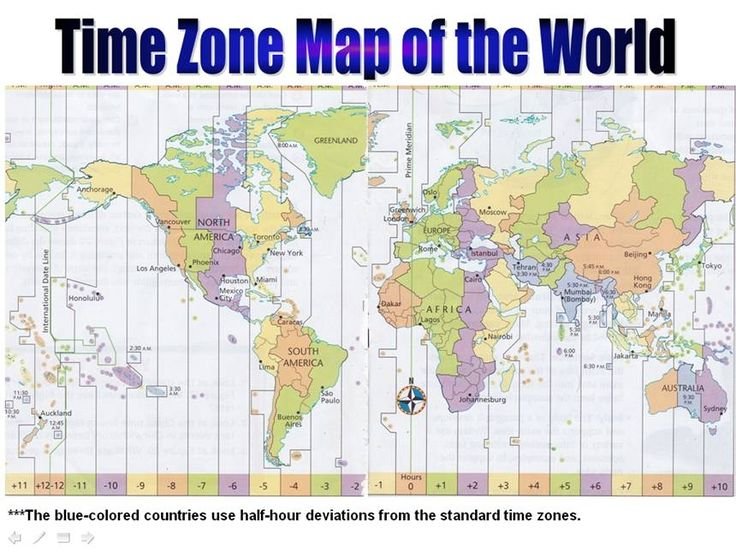
Have you ever wondered why the time is different in every country? Time zones are something we use daily, but how did they come about, and why are they so important? In this blog, we’ll explore the origins of time zones, how they work, and their impact on communication and the global economy.
The Origins of Time Zones: How Did It All Begin?
Before the introduction of time zones, every city had its own local time. This meant that each city would set its clocks based on the position of the sun in the sky. However, this system became increasingly problematic, especially with the rise of transportation and communication.
The concept of time zones was first introduced by Sir Sandford Fleming, a Canadian engineer, in the late 19th century. Fleming realized that having a standardized time across different regions of the world would be beneficial. This idea led to the International Meridian Conference in 1884, held in Washington, D.C., where it was decided that the world would be divided into 24 time zones. Each of these zones would be based on 15-degree increments of longitude, with the prime meridian (0° longitude) passing through Greenwich, England, as the reference point.
The decision to divide the world into 24 time zones made global communication and transportation much more efficient.
How Does the Time Zone System Work?
The world is divided into 24 time zones, and each zone covers 15 degrees of longitude. This division reflects the Earth’s rotation: as the Earth rotates 360 degrees every 24 hours, each hour represents 15 degrees of rotation.
For example:
When you move 15 degrees east or west, the time shifts by one hour.
The prime meridian at Greenwich Mean Time (GMT) is the baseline, and time zones are adjusted from there. As you move eastward from GMT, the time becomes later, and as you move westward, the time becomes earlier.
So, when it’s 12:00 PM (noon) in London (GMT), it could be 7:00 AM in New York (Eastern Standard Time, UTC -5) or 9:00 PM in Tokyo (Japan Standard Time, UTC +9).
Understanding how time zones work helps us navigate the world’s clock system and manage time effectively in our everyday lives, whether it’s for work, travel, or communication.
Impact of Time Zones on Communication
Time zones have a major impact on global communication. For example, in business, scheduling meetings and phone calls across different time zones can be tricky. You wouldn’t want to call someone in another country in the middle of the night or interrupt their workday with a call at an inconvenient hour.
Here’s an example:
If you’re in New York and you need to arrange a meeting with someone in Tokyo, you have to account for a 14-hour time difference. If it’s 9:00 AM in New York, it’s already 11:00 PM in Tokyo. Without considering time zones, businesses could face delays and miscommunication.
Solution: Fortunately, technology has made managing time zones much easier. Tools like calendar apps, world clocks, and time zone converters help individuals and businesses schedule calls and meetings efficiently, no matter where they are in the world. With a few clicks, you can set up a call that works for everyone involved, regardless of their location.
The Role of Time Zones in the Global Economy
Time zones also play a significant role in the global economy. Businesses, stock markets, and global trade all operate across different time zones, allowing for economic activity to continue 24 hours a day.
For instance:
Financial markets like the New York Stock Exchange open in the morning and close in the afternoon in New York, but by the time they close, markets in other parts of the world, like Asia and Europe, are still active.
The global supply chain operates across time zones, with companies in different parts of the world working around the clock to manufacture, distribute, and sell goods.
Because of time zones, the world is constantly “awake,” and business never truly stops. Technology has further accelerated this by enabling remote work, online trading, and international collaborations, all of which occur in real-time despite time differences.
The interconnectedness of global economies means that decisions made in one part of the world can have ripple effects that impact the rest of the world, regardless of the time zone.
Conclusion: Time Zones and Their Importance in Our Lives
Time zones are essential for organizing life on a global scale. They help us coordinate schedules, communicate effectively across borders, and ensure that economic activity continues smoothly around the clock. Without the system of time zones, managing international relationships, business operations, and even personal connections would be far more challenging.
The next time you’re scheduling a meeting across continents or traveling to a different time zone, you’ll have a better understanding of how these systems keep the world running. From Sir Sandford Fleming’s vision to the technology we use today, time zones are a key part of our globalized world.
