When it comes to mapping and navigation, one key concept is essential: coordinate systems. These systems allow us to determine precise locations on Earth’s surface. Let’s dive into how these coordinate systems work and their importance in mapping.
- What is a Coordinate System?
A coordinate system is a framework used to define the position of a point in space by using numbers. In mapping, these numbers help us pinpoint a specific location on Earth’s surface, which is crucial for navigation, geospatial analysis, and even GPS systems. - Geographic Coordinates: Latitude & Longitude
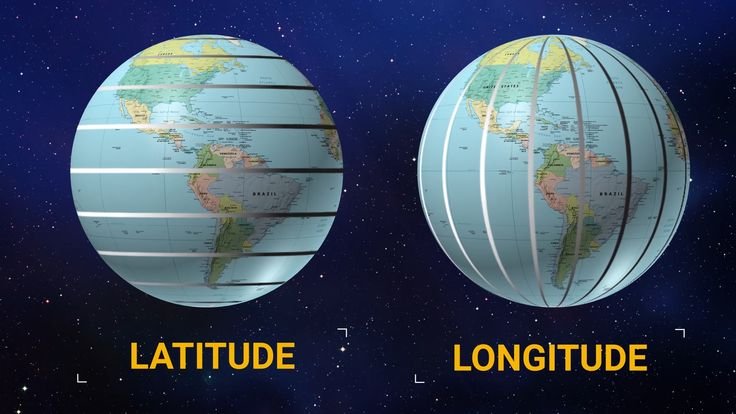
One of the most commonly used coordinate systems is the geographic coordinate system. It uses two main parameters:
Latitude: Measures the distance north or south of the equator (ranging from 0° at the Equator to 90° at the poles).
Longitude: Measures the distance east or west of the Prime Meridian (ranging from 0° to 180°).
These values help determine the exact position of any point on Earth, making them fundamental for navigation and mapping. Think of it like a grid that overlays the entire planet. - Cartesian Coordinates (3D)
Another type of coordinate system used in more advanced mapping is the Cartesian coordinate system. This system views Earth as a 3D sphere and uses three axes:
X-axis (horizontal)
Y-axis (vertical)
Z-axis (depth, or the distance toward the center of Earth)
This 3D system is commonly used for scientific modeling, such as in GIS (Geographic Information Systems), or for simulations that require precise measurements of Earth’s surface and internal structure. - Differences Between Geographic and Cartesian Coordinates
Both geographic and Cartesian coordinate systems serve different purposes:
Geographic Coordinates are primarily used for everyday applications, like mapping, GPS navigation, and global positioning.
Cartesian Coordinates are more commonly used in scientific research and advanced geospatial analysis, such as 3D modeling of the Earth or in satellite and aerospace technology.
Understanding these differences can help you choose the right system for the task at hand. - Conclusion
Knowing how coordinate systems work is crucial for creating accurate maps, navigating, and even understanding geographical data. Whether you’re using geographic coordinates to find your way with a map or Cartesian coordinates for advanced scientific research, these systems form the foundation of how we understand and navigate the world.
